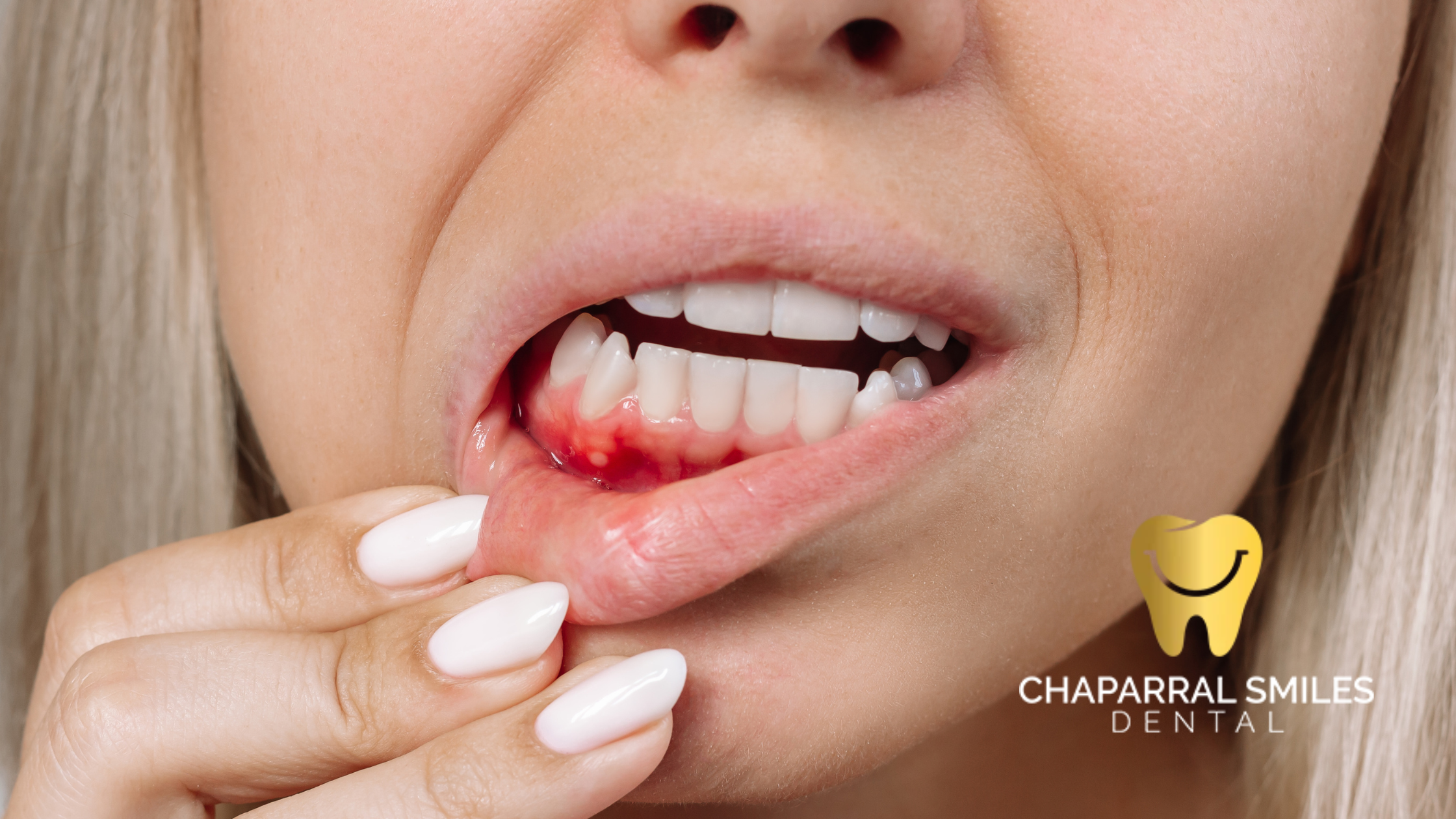
Because the mouth is a dynamic and bacteria-rich environment, proper healing of oral wounds is essential for maintaining overall health. Zinc plays a significant role in this process, supporting various stages of tissue repair and immune function.
Understanding how zinc contributes to wound healing can empower you to make informed decisions about your health. In this post, we will explore the mechanisms by which zinc aids in the healing process and discuss practical ways to incorporate it into your diet for optimal oral health.
Key Takeaways
- Zinc is essential for oral wound healing as it supports cell proliferation, collagen synthesis, and immune regulation—key elements in tissue repair.
- A deficiency in zinc can delay healing, increase infection risk, and worsen oral health outcomes after injury or surgery.
- Incorporating zinc-rich foods or supplements can speed recovery and improve oral health by enhancing enzyme activity and reducing inflammation.
The Biochemical Foundations of Zinc’s Role
Zinc plays a multifaceted role in oral wound healing through its biochemical properties. It is heavily involved in various metabolic processes, acting as a vital cofactor for numerous enzymes that contribute to tissue repair and regeneration.
As zinc levels decrease, your body’s ability to orchestrate these biochemical reactions diminishes, which may potentially delay wound closure and recovery.
Zinc as a Co-factor in Enzymatic Reactions
Zinc serves as a cofactor in over 300 enzymatic reactions within the body. This includes enzymes necessary for DNA and RNA synthesis, collagen synthesis, and the generation of reactive oxygen species, which are all vital during tissue repair.
“Without zinc, essential structural proteins like collagen can’t be synthesized efficiently, which could reduce the strength and integrity of your healing tissues.” – Dr. Kevin Kalin, Dentist in Calgary, Alberta
By facilitating the activity of these enzymes, zinc directly influences the efficiency of the healing process and tissue remodeling in oral wounds.
The Impact of Zinc on Cellular Functions
Your cells rely on zinc for optimal functionality, especially in the context of healing. Zinc enhances cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation—three key actions required for effective wound closure.
Additionally, it modulates inflammation, which can otherwise impede the healing process. This means that sufficient zinc not only aids in quicker recovery times but also ensures your oral tissue heals correctly, minimizing the risk of complications.
“Zinc is crucial for balancing inflammation—too much can slow healing, but with adequate zinc, your body can maintain a healthy inflammatory response to speed up tissue recovery.” – Dr. Kevin Kalin, Dentist in Calgary, Alberta
The impact of zinc on cellular functions is profound. For instance, it acts on keratinocytes, the primary cells found in the outer layer of the skin and oral mucosa, promoting their migration toward the wound site.
Zinc supports fibroblast activity, which is essential for producing collagen and the extracellular matrix, vital components that provide structure and strength to the newly formed tissue. Furthermore, zinc’s antioxidative properties help mitigate oxidative stress, fostering an environment conducive to healing.
Without adequate zinc, your cells may struggle to perform these imperative tasks, prolonging recovery or leading to suboptimal healing outcomes.
Zinc Deficiency and Its Consequences in Oral Healing
Lack of zinc in your diet can lead to serious consequences for oral wound healing. Zinc deficiency disrupts the natural processes of cell proliferation, collagen synthesis, and immune function, all of which are crucial for effective healing.
Individuals with low zinc levels may experience slower recovery from oral surgeries, increased risk of infections, and even exacerbated symptoms of oral diseases. This deficiency can create a cycle of poor nutrition and delayed healing, ultimately impacting your overall oral health.
The Link Between Low Zinc Levels and Delayed Healing
Low zinc levels are directly associated with delayed healing in oral wounds. Studies have demonstrated that insufficient zinc reduces fibroblast proliferation and impedes the formation of extracellular matrix components.
“If you’re recovering from oral surgery or dealing with frequent mouth ulcers, addressing zinc deficiencies could make all the difference in achieving faster, stronger healing outcomes.” – Dr. Kevin Kalin, Dentist in Calgary, Alberta
As a result, your body’s ability to repair tissues becomes compromised, leading to prolonged recovery and potential complications, such as delayed mucosal healing or chronic ulcers or necrotizing lesions. Ensuring adequate zinc intake can significantly enhance your healing processes.
Clinical Implications of Zinc Deficiency in Oral Wound Management
In the clinical setting, zinc deficiency requires careful consideration when managing oral wounds. Patients with inadequate zinc levels may respond poorly to standard wound care treatments, leading to strategies that must account for nutrient deficiencies.
Supplementation or dietary adjustments can be critical in these cases to facilitate effective healing and minimize postoperative complications. Health Canada recommends including zinc-rich foods such as lean meats, legumes, and fortified cereals as part of a balanced diet.
Clinicians should routinely assess zinc levels in patients presenting with delayed wound healing or recurrent oral lesions. When zinc deficiency is confirmed, incorporating zinc-rich foods or supplementation can promote faster recovery and enhance the overall outcome of oral procedures.
For example, an increase in dietary sources such as meat, shellfish, legumes, and nuts can elevate zinc levels, aiding in the acceleration of healing processes. As part of holistic care, understanding and addressing zinc deficiency will help in wound management and contribute to improved patient quality of life.
Mechanisms of Zinc in Tissue Repair
Zinc plays a pivotal role in tissue repair through multiple mechanisms that influence cellular processes vital for healing. It acts as a cofactor for various enzymes involved in DNA synthesis, protein synthesis, and cell division.
Additionally, zinc modulates oxidative stress responses, which can either protect or aggravate tissue injury depending on its concentration. Its presence facilitates the synthesis of collagen and other extracellular matrix components, critical for wound healing, while also influencing the behavior of various cell types involved in the repair process.
The Role of Zinc in Cell Proliferation and Migration
You may not realize it, but zinc directly influences your body’s ability to repair tissues by promoting cell proliferation and migration. These processes are vital to filling in wounds and regenerating damaged areas.
Specifically, zinc enhances the proliferation of fibroblasts and keratinocytes, both of which play key roles in wound healing. By supporting these actions, zinc helps expedite the healing process, allowing your mouth to recover more rapidly from oral injuries.
Zinc’s Influence on Inflammation and Immune Response
Zinc modulates inflammatory responses and immune function, two key components in wound healing. It helps control the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines while promoting the release of anti-inflammatory substances, thereby aiding in balancing the body’s response to injury.
This regulation is vital in limiting excessive inflammation that could delay healing and contribute to further complications.
Zinc’s involvement in the immune response extends beyond just inflammation. By supporting the development and function of various immune cells—including neutrophils and macrophages—it ensures that your body can effectively combat infections that may arise from oral wounds.
Studies have shown that zinc deficiency can lead to reduced immune cell functionality, increasing susceptibility to infections during the healing process. Ensuring adequate zinc intake can therefore accelerate healing and improve your overall resistance to complications associated with oral wounds.
Practical Applications of Zinc Supplementation
Incorporating zinc into your healing regimen can significantly enhance recovery from oral wounds. Supplementation may prove beneficial for those with dietary deficiencies or higher needs due to factors like surgery or injury.
Consult your healthcare provider for tailored guidance, ensuring proper dosing and monitoring while considering zinc-rich foods like nuts, seeds, and whole grains to bolster your intake naturally.
Recommended Dosages for Optimal Healing
For optimal healing, adults typically require 8-11 mg of zinc daily, with higher doses recommended for those healing from oral injuries. Studies suggest that taking 15-30 mg of zinc per day may accelerate tissue repair without surpassing the upper limit of 40 mg, which can lead to adverse effects.
Personal needs can vary, so a professional evaluation is advisable.
Forms of Zinc and Their Efficacy in Oral Health
Zinc comes in several forms, including zinc sulfate, zinc gluconate, and zinc citrate, each with varying rates of absorption and efficacy. Zinc gluconate and citrate are often preferred for oral health due to their superior bioavailability, promoting better wound healing and antimicrobial effects.
Choosing the right form can enhance both healing potential and overall health outcomes.
Zinc sulfate is the most commonly studied form, valued for its cost-effectiveness, but zinc gluconate and citrate provide better absorption. However, zinc sulfate may cause gastrointestinal discomfort in some individuals, making gluconate or citrate preferable for long-term use.
In clinical studies, zinc gluconate has demonstrated effective results in managing periodontal diseases and reducing oral microbial load.
Thus, opting for supplements with higher bioavailability can lead to more noticeable benefits in oral healing processes, making informed choices crucial for your health regimen.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Recent studies are shedding light on innovative uses of zinc in oral wound healing and disease management. These developments suggest that tailored zinc therapies could enhance healing rates and improve outcomes for various oral conditions.
As research continues to evolve, the exploration of zinc’s biochemical pathways promises to uncover new therapeutic targets and applications, allowing for more personalized treatment strategies in the future.
Innovations in Zinc Therapy for Enhanced Healing
Advancements in zinc therapy are paving the way for enhanced wound-healing applications. Formulations such as nano-zinc and sustained-release zinc supplements show promise for improving bioavailability and tissue absorption.
Clinical trials are investigating the optimal zinc concentrations and delivery systems, ultimately aiming to create more effective treatment protocols that speed up recovery and minimize complications following oral injuries.
The Potential of Zinc in Combating Oral Diseases
Zinc’s multifaceted role in oral health extends beyond wound healing; it also possesses potential for preventing and managing various oral diseases. Research indicates that zinc can inhibit bacterial growth and reduce inflammation, providing a dual mechanism of action against periodontal disease and other oral infections.
Furthermore, studies have suggested that zinc may play a role in regulating immune responses, which could contribute to better oral health outcomes and reduced incidence of diseases like gingivitis.
The potential of zinc in combating oral diseases is further highlighted by its effectiveness against common pathogens associated with oral infections. For instance, zinc formulations have demonstrated inhibitory effects on bacteria like Streptococcus mutans, which is a major contributor to dental caries.
Additionally, zinc’s anti-inflammatory properties can alleviate symptoms of periodontal disease, making it a crucial component of oral care products like mouthwashes and lozenges. Ongoing investigations into oral zinc supplementation continue to reveal promising results, suggesting that integrating zinc into your oral health regimen could provide a proactive approach in disease prevention and management.
Conclusion
Upon reflecting on the role of zinc in oral wound healing, you can see that this necessary mineral significantly influences the process. By supporting cellular proliferation, collagen synthesis, and immune function, adequate zinc levels can enhance your body’s natural healing capabilities.
Ensuring you have sufficient zinc in your diet can be beneficial, especially after oral injuries or surgeries. By understanding how zinc impacts your healing journey, you can take proactive steps to optimize your recovery and overall oral health.
Take the Next Step in Supporting Your Oral Health
If you’re recovering from a dental procedure or want personalized advice on improving your oral healing through nutrition, the team at Chaparral Smiles Dental is here to help. Located in SE Calgary, Alberta, we offer expert care tailored to your unique needs.
Have questions or ready to book your visit? Contact us today to schedule an appointment and let us support your journey to a healthier smile.
Reviewed by: Dr. Kevin Kalin